Jones and bartlett emt 12th edition – Jones & Bartlett EMT: 12th Edition is the definitive resource for emergency medical technicians (EMTs), providing a comprehensive overview of the roles, responsibilities, and standards of EMT practice. This authoritative guide offers an in-depth exploration of patient assessment and management, airway management and ventilation, trauma management, medical emergencies, special operations, and considerations for EMTs working in diverse environments.
With its clear and concise explanations, engaging case studies, and up-to-date information, Jones & Bartlett EMT: 12th Edition empowers EMTs with the knowledge and skills they need to provide exceptional patient care in the prehospital setting.
EMT Responsibilities and Standards

EMTs are healthcare professionals who provide emergency medical care in the prehospital setting. They are responsible for assessing and managing patients, providing life-saving interventions, and transporting patients to the hospital. EMTs must adhere to ethical and legal considerations, including patient confidentiality, informed consent, and the duty to provide care.
National and State Standards for EMT Practice, Jones and bartlett emt 12th edition
EMTs must meet national and state standards for practice. These standards include requirements for education, training, and certification. The National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) sets national standards for EMT certification. States may have additional requirements for EMTs working within their jurisdiction.
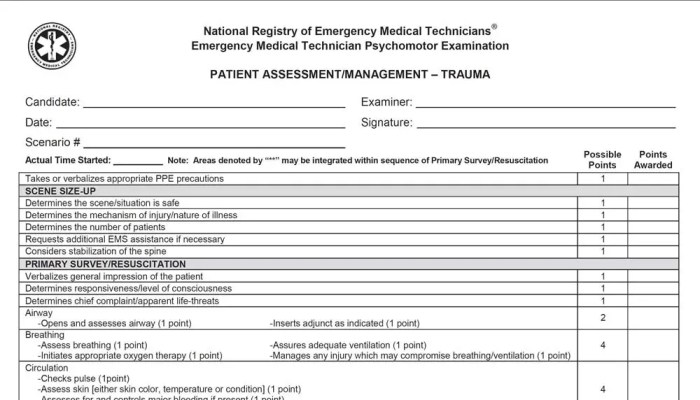
Patient Assessment and Management: Jones And Bartlett Emt 12th Edition
Patient assessment is the process of gathering information about a patient’s condition. EMTs use a variety of assessment techniques, including visual observation, palpation, auscultation, and percussion. EMTs must also be able to interpret vital signs and conduct a physical examination.
Scene Safety and Triage
EMTs must ensure scene safety before approaching a patient. This includes assessing for hazards, such as traffic, downed power lines, or hazardous materials. EMTs must also triage patients to determine the order in which they will be treated.
Airway Management and Ventilation

Airway management is the process of ensuring that a patient’s airway is open and clear. EMTs may use a variety of airway management techniques, including bag-valve-mask ventilation and endotracheal intubation.
Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy is the administration of oxygen to a patient. EMTs may use oxygen therapy to treat a variety of conditions, such as respiratory distress, cardiac arrest, and shock.
Trauma Management
Trauma management is the process of caring for a patient who has suffered a traumatic injury. EMTs must be able to assess and manage a variety of traumatic injuries, including head injuries, spinal injuries, and extremity injuries.
Types of Trauma
There are two main types of trauma: blunt trauma and penetrating trauma. Blunt trauma is caused by a force that does not break the skin, such as a fall or a motor vehicle accident. Penetrating trauma is caused by a force that breaks the skin, such as a gunshot wound or a stabbing.
Medical Emergencies
Medical emergencies are sudden, life-threatening conditions that require immediate medical attention. EMTs are trained to assess and manage a variety of medical emergencies, such as cardiac arrest, stroke, and diabetic emergencies.
Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest is a sudden loss of heart function. EMTs must be able to recognize and manage cardiac arrest. Treatment for cardiac arrest includes CPR and defibrillation.
Special Operations and Considerations
EMTs may be called upon to work in a variety of special operations, such as disaster response and hazardous materials handling. EMTs must be trained to use special equipment and techniques in these situations.
Disaster Response
EMTs may be called upon to respond to disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and terrorist attacks. EMTs must be able to work in chaotic and dangerous conditions.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the key responsibilities of EMTs?
EMTs are responsible for providing immediate medical care to patients in the prehospital setting. This includes assessing patients’ conditions, providing basic life support, administering medications, and transporting patients to the hospital.
What are the ethical and legal considerations for EMTs?
EMTs must adhere to ethical principles, such as patient confidentiality, autonomy, and beneficence. They must also be aware of the legal implications of their actions, including informed consent, negligence, and assault.
What are the national and state standards for EMT practice?
EMTs must meet national and state standards for certification and practice. These standards include requirements for education, training, and continuing education.