Introducing the Biomolecules Video Handout Answer Key, a comprehensive guide that unlocks the mysteries of life’s fundamental components. Delving into the depths of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, this answer key provides a clear understanding of their functions, interactions, and applications.
This handout serves as a valuable resource for students, educators, and anyone seeking to unravel the complexities of biomolecules and their indispensable role in the living world.
Introduction
Biomolecules are the building blocks of life. They are organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and sometimes nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. Biomolecules are essential for all life processes, including energy storage and release, structural support, cell signaling, and genetic information.
Examples of biomolecules include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Types of Biomolecules
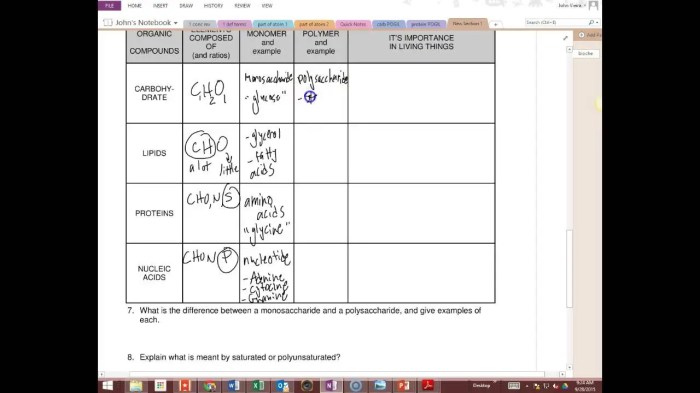
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They are classified into three main types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharides linked together, such as sucrose and lactose.
Polysaccharides are composed of many monosaccharides linked together, such as starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
Lipids
Lipids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and sometimes nitrogen and phosphorus. They are classified into two main types: fats and oils. Fats are solid at room temperature, while oils are liquid. Lipids are important for energy storage, insulation, and hormone production.
Proteins
Proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. They are composed of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. Proteins are essential for a wide range of functions, including structural support, enzyme catalysis, and cell signaling.
Nucleic acids, Biomolecules video handout answer key
Nucleic acids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. They are composed of nucleotides linked together by phosphodiester bonds. Nucleic acids are essential for storing and transmitting genetic information.
Functions of Biomolecules
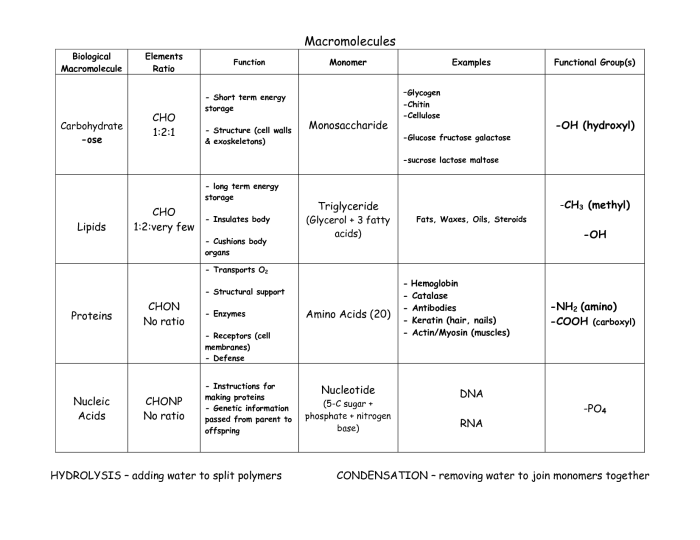
Energy storage and release
Carbohydrates and lipids are the main sources of energy for cells. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then used to produce energy through cellular respiration. Lipids are stored in fat cells and can be broken down into fatty acids and glycerol to produce energy.
Structural support
Proteins and carbohydrates provide structural support for cells and tissues. Proteins form the cytoskeleton, which gives cells their shape and support. Carbohydrates form the cell wall in plants and the extracellular matrix in animals.
Cell signaling
Proteins and lipids are involved in cell signaling. Proteins can bind to receptors on the surface of cells, which triggers a cascade of events that can lead to changes in gene expression, protein synthesis, or cell behavior. Lipids can also bind to receptors on the surface of cells and trigger changes in cell behavior.
Genetic information
Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information. DNA contains the instructions for making all of the proteins in a cell. RNA is involved in protein synthesis and gene expression.
Biomolecule Interactions
Biomolecules interact with each other in a variety of ways. These interactions can be covalent bonds, noncovalent bonds, or electrostatic interactions. Covalent bonds are the strongest type of bond and are formed when two atoms share electrons. Noncovalent bonds are weaker than covalent bonds and include hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic interactions.
Electrostatic interactions are caused by the attraction or repulsion of charged particles.
Biomolecules also interact with the environment. For example, proteins can bind to water molecules, which helps to stabilize their structure. Lipids can form membranes that surround cells and organelles.
Biomolecule interactions are essential for all life processes. They allow biomolecules to form complex structures, such as proteins and nucleic acids, and to interact with each other to carry out cellular functions.
Applications of Biomolecules: Biomolecules Video Handout Answer Key
Biomolecules have a wide range of applications in biotechnology, medicine, and agriculture.
Biotechnology
Biomolecules are used in biotechnology to produce a variety of products, including pharmaceuticals, biofuels, and biomaterials. For example, recombinant DNA technology is used to produce human insulin, which is used to treat diabetes.
Medicine
Biomolecules are used in medicine to diagnose and treat diseases. For example, antibodies are used to diagnose and treat cancer. Gene therapy is used to treat genetic diseases by introducing healthy genes into cells.
Agriculture
Biomolecules are used in agriculture to improve crop yields and resistance to pests and diseases. For example, genetically modified crops are designed to resist pests and diseases, which can reduce the need for pesticides and herbicides.
Query Resolution
What is the primary function of carbohydrates in living organisms?
Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy for cells and provide structural support to organisms.
How do lipids contribute to cell function?
Lipids play a crucial role in cell membranes, providing a barrier and regulating the passage of substances. They also serve as energy storage and signaling molecules.
What is the unique property of proteins that enables them to perform diverse functions?
Proteins possess a wide range of amino acid sequences, which allows them to adopt specific shapes and interact with other molecules, enabling them to carry out a vast array of functions.
How do nucleic acids differ from other biomolecules?
Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) carry genetic information and play a vital role in protein synthesis and cellular processes.